So What's Inside? Well.....
So when it comes to robotic prosthetics, one question comes to mind. How do the amputees control the prosthetic? Well, the answer is simpler than you think. When robotic prosthetics are installed, an array of electrodes are implanted in the parts of the brain that controlled the lost limbs. To put it in more simplified terms, artificial neurons are installed and they act as though they are your old ones. The software has a big role to play in that array as it serves as the instructions when it comes to the connection to the prosthetic, basically telling it which set of wires and motors to activate. It even is getting a major upgrade to include replicating the feeling of touch, primarily by a research team at the University of Chicago.
When discussing the hardware and wiring of these prosthetics, one thing is for sure, beyond a shadow of a doubt. They definitely are not using car batteries to power these prosthetics and are certainly not using large motors found on crains to move the joints. So what are they using? Well when it comes to the motors, it all depends on how small the joints are. When it comes to small joints,like for toes and fingers, small DC motors are the most popular and best choice as they are quite small as well as quiet.This is what one looks like.

When it comes to the wiring of these prosthetics, it must be flexible or else overtime they will wear out and start to tear in some places. Some German researchers found this to be quite the opportunity and created wire that acts as artificial muscle. When it comes to activating it, all that is needed is the array of electrodes planted in the amputee's brain, as they send enough electricity through out the proshetic to activate the artificial muscle. This artificial muscle keeps the prosthetic lightweight by being sleek in design as well as thin, yet durable.
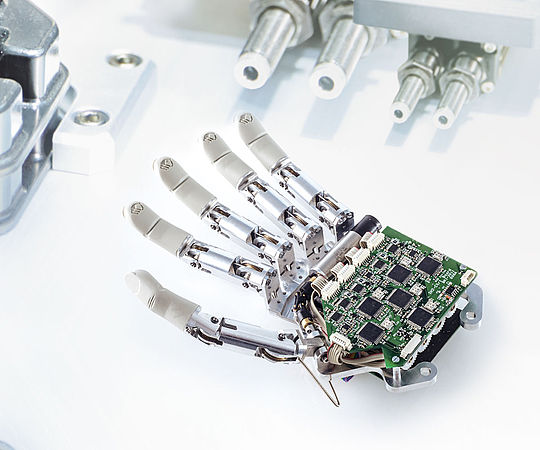
This is a prosthetic hand with its interior parts exposed. As you can clearly see, a circuit board in charge of helping the electric signals get to the motors in the hands small DC motor joints is clearly present and nicely secured in place.